Nautobot ChatOps Installation Guide¶
This guide outlines the process of enabling Nautobot ChatOps, which includes:
- Nautobot ChatOps Installation Guide
- Prerequisites
- Chat Platforms Configuration
- Installation Guide
- Configuration Guide
- Granting Access to the Chat Platform
- Link Nautobot Account
- Test Your Chatbot
- Integrations Configuration
Glossary¶
- Chat Platform: A communication service (e.g., Mattermost, Microsoft Teams, Slack, Cisco Webex).
- Command: A particular instruction sent by users via the Chat Platform, which is then processed by an Integration.
- Dispatcher: A class specific to the Chat Platform that processes incoming chat messages, executes commands, and sends results back to the Chat Platform.
- Integration: A component that defines commands, handles data retrieval, and manipulation for specific tools or services (e.g., IP Fabric, AWX / Ansible Tower, Palo Alto Panorama, Grafana, Cisco ACI, Cisco Meraki, Arista CloudVision).
- Platform View: A Django View designed to handle Chat Platform data.
- Sub-command: An instruction that is nested within a Command.
- Worker: A module within an Integration, designed to handle and process a Command, receiving data from Platform Views and returning results via a Dispatcher's generic API.
Prerequisites¶
Ensure the following before beginning the installation:
- Nautobot 1.5.4 or higher is installed.
- Your chat platform can access Nautobot via an HTTPS URL.
- Some chat platforms require SSL certificate verification to communicate with the Nautobot server.
- For development, you may use HTTP.
- You have
sudoaccess on the Nautobot server. - You have administrative access within the Nautobot Web UI.
Potential Apps Conflicts¶
Warning
If upgrading from 1.x version to 2.x version of nautobot-chatops App, note that it now incorporates features previously provided by individual apps.
Conflicting Apps list:
nautobot_plugin_chatops_acinautobot_plugin_chatops_ansiblenautobot_plugin_chatops_arista_cloudvisionnautobot_plugin_chatops_ipfabricnautobot_plugin_chatops_grafananautobot_plugin_chatops_merakinautobot_plugin_chatops_panorama
To prevent conflicts during nautobot-chatops upgrade:
- Remove conflicting applications from the
PLUGINSsection in your Nautobot configuration before enabling the latestnautobot-chatopsversion. - Transfer the configuration for conflicting apps to the
PLUGIN_CONFIG["nautobot_chatops"]section of your Nautobot configuration. Seedevelopment/nautobot_config.pyfor an example. Each integration set up guide contains a chapter with upgrade instructions. - Remove conflicting applications from your project's requirements.
These steps will help prevent issues during nautobot-chatops upgrades. Always back up your data and thoroughly test your configuration after these changes.
Warning
If conflicting Apps remain in PLUGINS, the nautobot-chatops App will raise an exception during startup to prevent potential conflicts.
Chat Platforms Configuration¶
The nautobot-chatops package supports multiple chat platforms.
Set up your chosen chat platform:
Installation Guide¶
Note
Install the App manually or via Python's pip. For detailed information, visit the Nautobot documentation. The pip package for this App is nautobot-chatops.
Warning
Follow the Nautobot App Installation Instructions for complete and most recent guidelines.
Install Guide¶
Note
Apps can be installed from the Python Package Index or locally. See the Nautobot documentation for more details. The pip package name for this app is nautobot-chatops.
The app is available as a Python package via PyPI and can be installed with pip:
To use specific integrations, add them as extra dependencies:
To auto-install Nautobot ChatOps during future upgrades, add nautobot-chatops to local_requirements.txt (create if not
present) in the Nautobot root directory, adjacent to requirements.txt:
After installation, enable the App in your Nautobot configuration by updating your nautobot_config.py file:
- Include
"nautobot_chatops"in thePLUGINSlist. - Add the
"nautobot_chatops"dictionary toPLUGINS_CONFIGand override defaults if necessary.
# In your nautobot_config.py
PLUGINS = ["nautobot_chatops"]
PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
"nautobot_chatops": {
# ADD YOUR SETTINGS HERE
}
}
Added in version 3.0.0
Some configuration settings have now been added to the Nautobot Admin Config page. See Nautobot Admin
Configuration Guide¶
Adjust the App's behavior with the following settings:
| Configuration Setting | Description | Mandatory? | Default | Available on Admin Config |
|---|---|---|---|---|
delete_input_on_submission |
Removes the input prompt from the chat history after user input | No | False |
No |
restrict_help |
Shows Help prompt only to users based on their Access Grants | No | False |
No |
send_all_messages_private |
Ensures only the person interacting with the bot sees the responses | No | False |
No |
fallback_chatops_user |
Nautobot User for Chat Commands to use if the user has not linked their account | Yes | chatbot |
Yes |
session_cache_timeout |
Controls session cache | No | 86400 |
No |
Granting Access to the Chat Platform¶
Nautobot provides an HTTP endpoint(s) for each supported chat platform. Although these endpoints do implement authentication to prevent arbitrary HTTP requests from triggering bot actions, they can accept and act on any validly-formed request from the chat platform, which could originate from any organization, team, channel(room), or user who has access to the chat system.
For most realistic deployments, open and unrestricted access to the bot from any chat account is undesirable. Therefore, in this version, access to the chatbot defaults to "deny all" when initially installed, but varying scopes (per organization, per channel, per user) and degrees (all commands, all sub-commands of a single command, single sub-command of a single command) of access can be granted through Nautobot.
The access grants are maintained in Nautobot's database for persistence, and are change-logged like other Nautobot records.
Note that access grants are based on the chat platform's internal ID values for users, channels, and organizations; although you can and should attach a user-friendly name to each access grant for reference, it is the ID value that is actually enforced by Nautobot. On some platforms and for some access scopes, the Nautobot UI "Look up Value from Name" button can be used to auto-discover the ID value corresponding to a given name; if this fails, you can always attempt to send a request to Nautobot from the desired user/channel/organization and retrieve the ID value from the resulting error message to use to define a new access grant.
The specific access grants you will want to define will depend on your operational requirements, but some examples are provided below to help you get started.
Example: Unrestricted Access Within a Single Organization¶
In the simplest realistic configuration example, access to all chatbot commands is granted for all users and all channels in a single organization scope.
| Command | Sub-command | Grant type | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
* |
* |
organization | my-org | T202B88NN |
* |
* |
channel(room) | any | * |
* |
* |
user | any | * |
Example: Split Command Access to Different Channels¶
In this example, Nautobot is providing two separate command groupings, each of which is intended for use by a different team within the organization. Each team has a dedicated channel on the chat platform, to which access is already controlled by other means, so we can allow all users within a given channel access.
| Command | Sub-command | Grant type | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
* |
* |
organization | my-org | T202B88NN |
support |
* |
channel(room) | support | C2020H455 |
devops |
* |
channel(room) | devops | C3030I566 |
* |
* |
user | any | * |
Example: Restrict Specific Command and Sub-command to Specific Users in a Specific Channel¶
In this example, Nautobot has a potentially-destructive sub-command that should only be used by a handful of admin users. Other sub-commands under this sub-command can be used by anyone in the devops channel. Other commands are harmless fun and can be used by any user in the organization in any channel.
| Command | Sub-command | Grant type | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
* |
* |
organization | my-org | T202B88NN |
jokes |
* |
channel(room) | any | * |
jokes |
* |
user | any | * |
network |
* |
channel(room) | devops | C3030I566 |
network |
history |
user | any | * |
network |
redeploy |
user | admin1 | U2049K991 |
network |
redeploy |
user | admin2 | U2039K725 |
network |
redeploy |
user | admin3 | U7924K784 |
network |
status |
user | any | * |
weather |
* |
channel(room) | any | * |
weather |
* |
user | any | * |
Link Nautobot Account¶
Added in version 3.0.0
Nautobot ChatOps now uses the built-in Nautobot permissions for Nautobot Objects (Devices, Locations, Racks, etc.). Each user will need to link their Nautobot Account with their Chat Platform User Account. Login to Nautobot then access the Link ChatOps Account within the Plugins menu. Here you can provide your email address and select the ChatOps Platform you are using, then click the Look up User ID from Email to get your Chat User ID.
A Nautobot user can have multiple Chat users connected, but the Chat User can only be linked to one Nautobot user. As an example my team is transitioning from Slack to Mattermost. My Slack User ID and my Mattermost User ID can both be connected to the same Nautobot User.
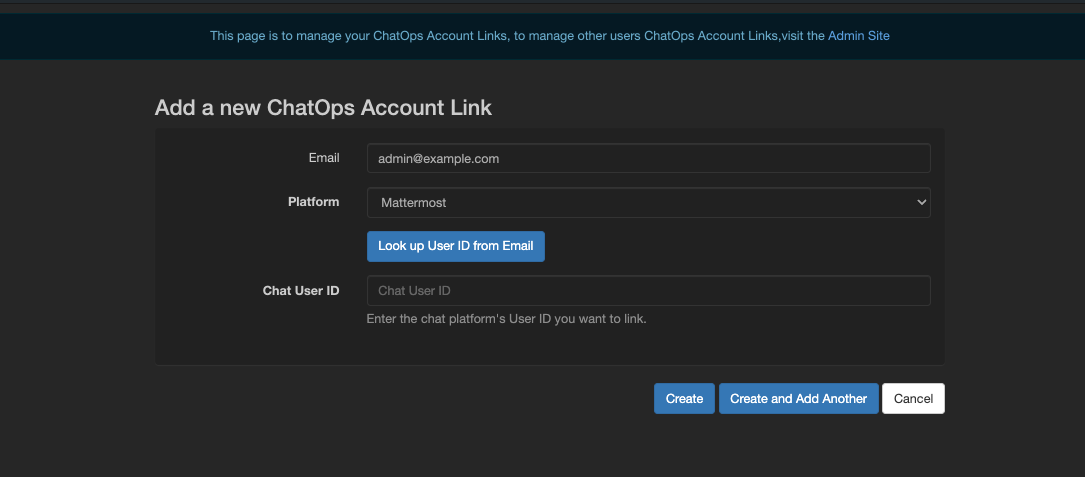
Configuring Account Link for many users¶
Admins have the ability to access the Nautobot Admin page and can use ChatOps Account Links page to link multiple accounts, but you will need to know the Chat Platforms user IDs for each user you are linking.
Test Your Chatbot¶
Finally, test your chatbot's functionality within your chosen chat application, using a command like /nautobot get-devices.
Integrations Configuration¶
The nautobot-chatops package includes multiple integrations. Each requires extra dependencies defined in pyproject.toml. See the installation guide for instructions on installing these dependencies.
Set up integrations using the specific guides: