Adding REST API Endpoints¶
Apps can declare custom endpoints on Nautobot's REST API to retrieve or manipulate models or other data. These behave very similarly to views, except that instead of rendering arbitrary content using a template, data is returned in JSON format using a serializer. Nautobot uses the Django REST Framework, which makes writing API serializers and views very simple.
First, create a serializer for the Animal model, in api/serializers.py:
# api/serializers.py
from nautobot.apps.api import ValidatedModelSerializer
from nautobot_animal_sounds.models import Animal
class AnimalSerializer(ValidatedModelSerializer):
"""API serializer for interacting with Animal objects."""
class Meta:
model = Animal
fields = ('id', 'name', 'sound')
Tip
For more full-featured models, you should use one of the other base classes from nautobot.apps.api such as NautobotModelSerializer.
Next, create a generic API view set that allows basic CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) operations for Animal instances. This is defined in api/views.py:
# api/views.py
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from nautobot_animal_sounds.models import Animal
from .serializers import AnimalSerializer
class AnimalViewSet(ModelViewSet):
"""API viewset for interacting with Animal objects."""
queryset = Animal.objects.all()
serializer_class = AnimalSerializer
Tip
For more full-featured models, you should probably use nautobot.apps.api.NautobotModelViewSet as a base class.
Finally, register a URL for our endpoint in api/urls.py. This file must define a variable named urlpatterns.
# api/urls.py
from rest_framework import routers
from .views import AnimalViewSet
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register('animals', AnimalViewSet)
urlpatterns = router.urls
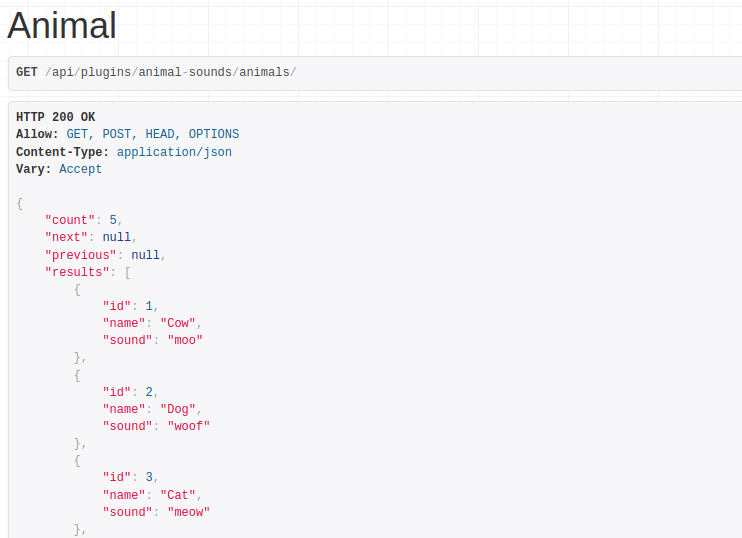
With these three components in place, we can request /api/plugins/animal-sounds/animals/ to retrieve a list of all Animal objects defined.
Warning
This example is provided as a minimal reference implementation only. It does not address authentication, performance, or the myriad of other concerns that app authors should have.