Firewall Models Reference¶
This plugin follows hierarchical approach to the modeling of the firewall objects. The aim is to provide flexible framework for building firewall policies.
Child objects associated to their parents via many-to-many relationship can be deleted only once the parent object is gone. This prevents accidental changes to firewall policies.
For example, this would apply to an IP Address object used in an Address Object, which in turn is one of the descendants of a Policy object. That IP Address could NOT be deleted until one of the below happened:
- The relationship between IP Address and the Address Object is removed
- The Address Object is deleted
To reiterate, this acts as a protection mechanism to prevent unintentional object deletions.
All the data models introduced by the Firewall plugin support the following Nautobot features:
- Rest API
- GraphQL
- Custom fields
- Custom Links
- Relationships
- Change logging
- Custom data validation logic
- Webhooks
The below diagram shows hierarchy of the models, and how they relate to one another. Policy model is at the top of the hierarchy; it has no parents. Every other model is in the child-parent relationship with the preceding model, moving from left to right.
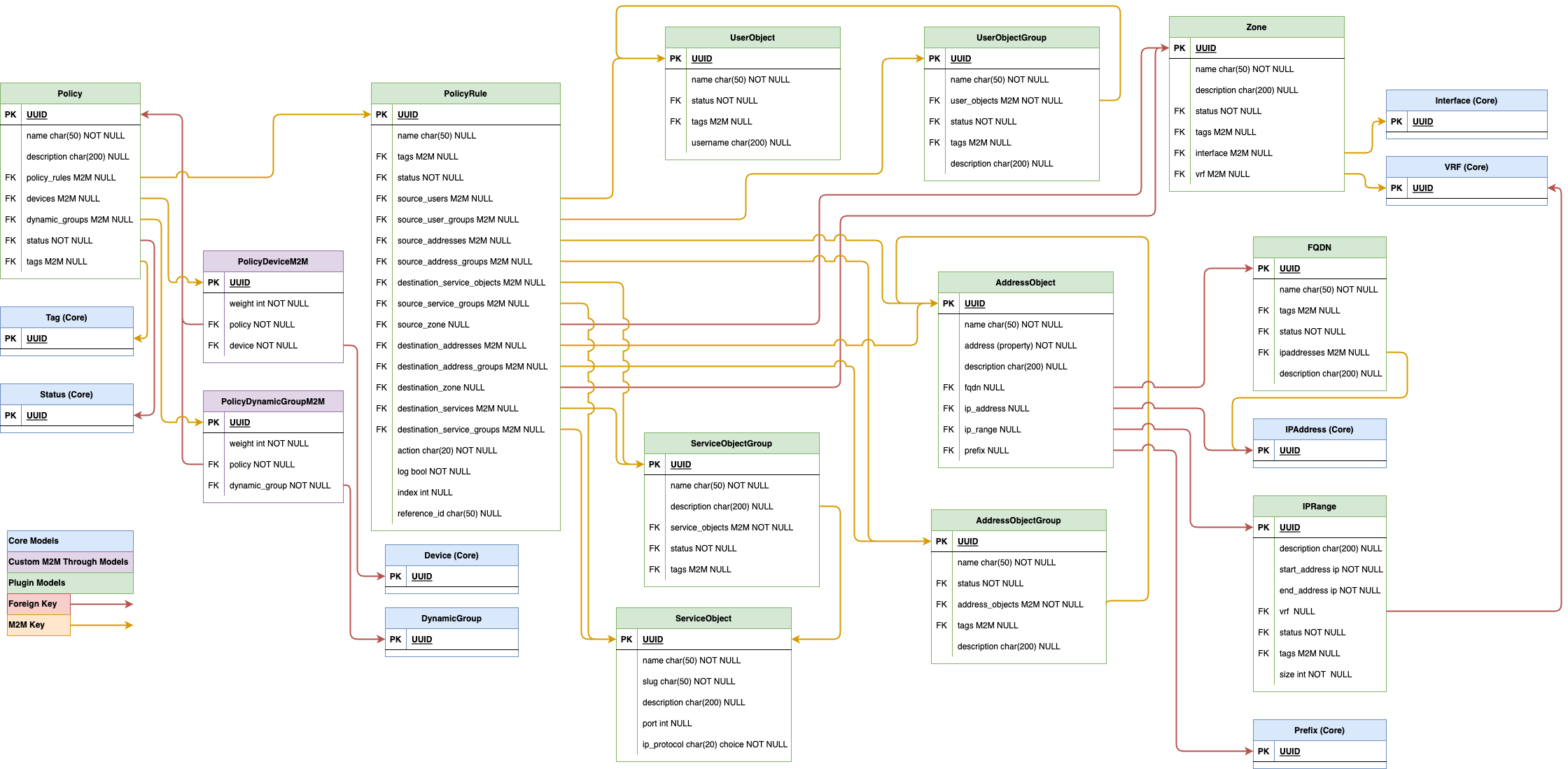
Creation Order¶
The simplest approach to creating policies is to work upwards, starting with the objects at the bottom of the hierarchy.
- If you require Address Objects, create the underlying objects first. For example, ensure IP Address is in place before you create an Address Object for that IP.
- Create the bottommost child objects, Address Objects, User Objects and ServiceObjects.
- Optionally create groups, Address Object Groups, User Object Groups and ServiceObjectGroups.
- Groups are commonly used to aggregate objects of the same type in firewall policies.
- Create Policy Rules.
- Create Policy and assign indexes to rules.
- Add Device and/or DynamicGroup objects to a Policy.
Custom Many-To-Many Models¶
This plugin uses custom models to model many-to-many relationships (also known as through models). Some of these models implement the logic for deleting objects in child-parent relationships, as discussed earlier. Other models add attributes enriching relationships defined between objects.
PolicyRuleM2M, PolicyDeviceM2M, PolicyDynamicGroupM2M are used for setting additional attributes and the remainder are solely defined for the disabling deleting from the bottom up.
Available Models¶
{% include-markdown "./models/policy.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/policydevicem2m.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/policydynamicgroupm2m.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/policyrule.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/serviceobject.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/serviceobjectgroup.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/userobject.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/userobjectgroup.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/addressobject.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/addressobjectgroup.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/applicationobject.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/applicationobjectgroup.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/fqdn.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/iprange.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/zone.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/natpolicy.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/natpolicyrule.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/natpolicydevicem2m.md" heading-offset=2 %}
{% include-markdown "./models/natpolicydynamicgroupm2m.md" heading-offset=2 %}